Early Jurassic: the Dinosaurs spread across Pangaea
Great plant-eating dinosaurs roaming the earth, feeding on lush growths of ferns and palm-like cycads and bennettitaleans, smaller but vicious carnivores stalking the great herbivores, oceans full of fish, squid, and coiled ammonites, plus great ichthyosaurs and long-necked plesiosaurs, vertebrates taking to the air, like the pterosaurs and the first birds. . . this was the Jurassic Period, beginning approximately 210 million years ago and lasting for 70 million years of the Mesozoic Era.
 Named for the Jura Mountains on the border between France and Switzerland, where rocks of this age were first studied, the Jurassic has become a household word with the success of the movie Jurassic Park. Outside of Hollywood, the Jurassic is still important to us today, both because of its wealth of fossils and because of its economic importance -- the oilfields of the North Sea, for instance, are Jurassic in age.
Named for the Jura Mountains on the border between France and Switzerland, where rocks of this age were first studied, the Jurassic has become a household word with the success of the movie Jurassic Park. Outside of Hollywood, the Jurassic is still important to us today, both because of its wealth of fossils and because of its economic importance -- the oilfields of the North Sea, for instance, are Jurassic in age.
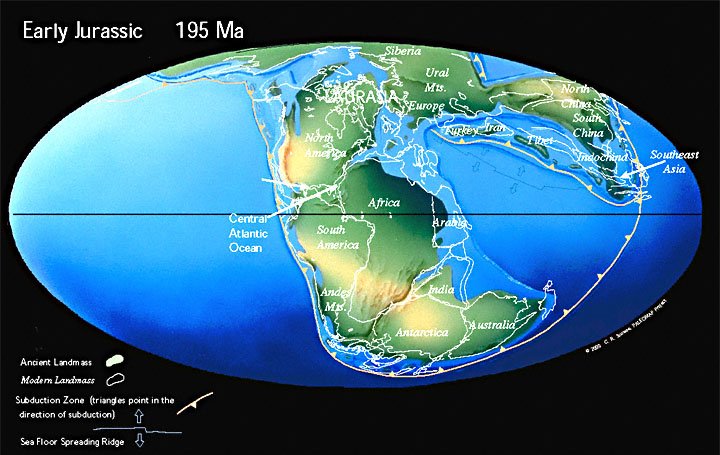
By the Early Jurassic, south-central Asia had assembled. A wide Tethys ocean separated the northern continents from Gondwana. Though Pangaea was intact, the first rumblings of continental break up could be heard.
Pangaea was assembled piece-wise. The continental collisions that lead to the formation of the super-continent began in the Devonian and continued through the Late Triassic.
In a similar fashion, the super-continent of Pangaea did not rift apart all at once, but rather was subdivided into smaller continental blocks in three main episodes. The first episode of rifting began in the middle Jurassic, about 180 million years ago. After an episode of igneous activity along the east coast of North America and the northwest coast of Africa, the Central Atlantic Ocean opened as North America moved to the northwest (See Jurassic). This movement also gave rise to the Gulf of Mexico as North America moved away from South America. At the same time, on the other side of Africa, extensive volcanic eruptions along the adjacent margins of east Africa, Antarctica, and Madagascar heralded the formation of the western Indian Ocean.
During the Mesozoic North America and Eurasia formed one landmass, sometimes called Laurasia. As the Central Atlantic Ocean opened, Laurasia rotated clockwise, sending North America northward, and Eurasia southward. Coals, which were abundant in eastern Asia during the early Jurassic, were replaced by deserts and salt deposits during the Late Jurassic as Asia moved from the wet temperate belt to the dry subtropics. This clockwise, see-saw motion of Laurasia also led to the closure of the wide V-shaped ocean, Tethys that separated Laurasia from the fragmenting southern super-continent of Gondwana.
Please click here to complete it